What Are Microplastics? Microplastics in Our Drinks

Author: Sumana Rao | Posted on: February 26, 2026


“The biggest obstacle in our lives are the one that mind creates”
Every opportunity that we get in our one life can take us towards our goal. One opportunity that we get can make a difference between an extraordinary life and mediocre one.
We all get many opportunities life, we miss some and can take some. Sometimes it depends on the circumstances in our life to pick or not to pick an opportunity. Most times we hesitate to take advantage of an opportunity that is staring at us.
What we always don’t think or realize is – we all have one life and if we miss opportunities then we may not get another one. Yes, it is hard to make decisions that can change our lives for better as we don’t know where it takes us. However, if we don’t pick an opportunity we may regret for not taking a decision.
How to prepare to exploit opportunities?
1. Look for an opportunity: Opportunities don’t last forever. When there is one, take steps to make sure you don’t miss out on something that can change your life for good. Or at least give it a try and see how you feel.
2. Saying yes often: When opportunities come around say yes and give it a try. When you get a chance to exhibit your talent grab it. Give it a try, negotiate & if you don’t like the experience you can always look for something else. It is not easy, but who knows – you may achieve success!
Instead of sitting and worrying on day to day to life – if you get an opportunity to travel and if you can afford why not? You may not get a chance to travel again to same place. Explore new places, try new things & find your inner peace!
3. Try new things: Be open to new ideas and be open to it. It is like trying new food. You may initially hesitate but once you know how good the food and what benefit you get then you won’t hesitate to try it again.
4. Risk and opportunity: Always remember – opportunities and risk always go hand in hand, they go together. The best opportunity is always the riskiest one. Starting a business is not everyone’s cup of tea. But if you have insight, goal and hardworking and, if an opportunity is waiting for you then take some risk in your life. It is a combination of risk and opportunity where, don’t forget money is also involved. We have examples of people opted for such risks and made it a success in life.
5. Meet and talk to people: Develop a friendly attitude that boosts your people circle. When you develop your network, it gives exposure to more and more opportunities. When you talk to people they may share their vision, ideas or may become your guide/mentor for a successful and happy life.
6. Don’t be afraid and don’t hesitate: Opportunities don’t come often in your way. One need to be very fast to grab it before it goes to someone else. Discuss with your friends, partners, family members and decide. Don’t forget that there are other people who wait for ‘that kind of opportunity’ and you may lose out.
7. A positive attitude helps: Don’t imagine negative or setbacks before you proceed. If so, you won’t be able to take risk and go nowhere in life. Success often depends on positive attitude and energy with which you can win heart of many people. Positive attitude gives confidence to you as well as to the people (in you) who provide opportunity for you!
8. Focusing and sticking to goal: When you are not focused, or don’t know what is your focus in life, then you will not recognize the opportunity in your hand. Understand what you want to do in life and take it to that direction. If you know your goal, then stick to it. Focus, determination and sticking to the goal always will give more opportunities and, you will feel that opportunities are created for you when you start seeing them in many numbers. If you know what you want out of life, your mind will focus in on that and be on the lookout when an opportunity arises.
Don’t be passive in life. Be creative and curious that helps you to understand the opportunities of life for better. Don’t be afraid to make mistakes in life. Getting scared to do anything is a step to failure in life. Remember by doing mistakes one will learn and gain experience. Whether it is right or wrong, looking for an opportunity and exploring new things in life helps you to grow and be a better person. Opportunity comes for prepared mind as it can recognize it.
.
Reference: www.werindia.com
.
Sauerkraut bread and sourdough bread differ mainly in their ingredients and fermentation process. Sauerkraut bread incorporates fermented cabbage (sauerkraut) into the dough, adding tangy flavor, moisture, and potential probiotic benefits. Sourdough bread is made with a fermented flour-and-water starter, relying on wild yeast and lactic acid bacteria for leavening, which gives it a chewy texture and distinctive sour taste.
Sauerkraut bread:
Sourdough bread:
Main differences: Sauerkraut bread is about adding fermented cabbage for flavor and nutrition, while sourdough bread is about using fermentation itself to rise and transform the dough.
| Aspect | Sauerkraut Bread | Sourdough Bread |
| Fermentation source | Sauerkraut (fermented cabbage) | Starter (fermented flour + water) |
| Leavening | Yeast or starter + sauerkraut | Wild yeast + bacteria in starter |
| Flavor | Tangy, savory, moist | Tangy, sour, chewy |
| Nutrients | Vitamin C, fiber, probiotics (partially retained) | Easier digestion, mineral bioavailability |
| Tradition | Central/Eastern European | Ancient Egyptian, global artisanal |
Which is better sauerkraut bread or sourdough bread?
It really depends on what you mean by better—nutrition, digestion, or taste. Both sauerkraut bread and sourdough bread have unique strengths, and they shine in different areas.
Sauerkraut Bread
Sourdough Bread
Which bread is “better”?
Overall -Sourdough bread is generally higher in protein and easier to digest, while sauerkraut bread adds Vitamin C and tangy flavor but has fewer live probiotics after baking.
Image credit: Image by Nils from Pixabay (Free to use under Pixabay content license, published on February 7, 2021)

Bubble fun is an engaging activity for kids, but it’s important to ensure their safety while enjoying this playtime. Here are some tips to have safe bubble fun with kids:
By following these safety tips, you can ensure that bubble play remains a fun and enjoyable activity for kids while minimizing potential risks. Always prioritize safety and supervise children during playtime to create a safe and positive experience.
Image credit: https://pxhere.com/en/photo/868580 CC0 Public Domain (uploaded
02/27/2017)
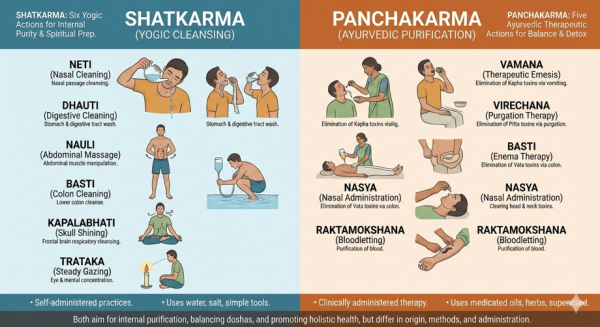
Panchakarma is Ayurveda’s deep detox and rejuvenation system. It’s not a home remedy or a quick cleanse — it’s a structured medical therapy meant to remove disease from the root.
Why Panchakarma is done?
Panchakarma is used to:
Unlike Shatkarma, Panchakarma works at tissue and cellular level.
Based on your body type and condition, Ayurvedic practitioners can guide you which treatment is better for you.
References:
Featured Image Credit: AI-generated image created with Google Gemini, February 10, 2026
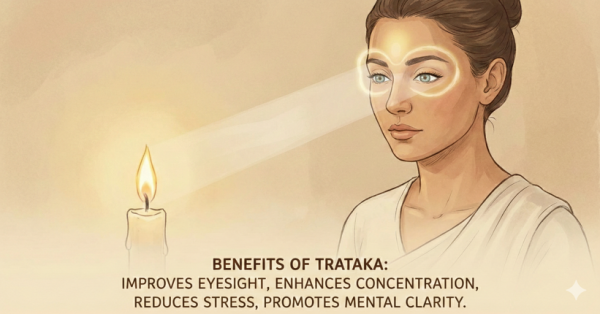
Steady gazing at a candle or point without blinking is known as Trataka. Unblinking focus on candle flame is the widespread practice that improves eye health.
What it cleanses?
Benefits
Ayurvedic effect: Calms Vata and Pitta, improves mental clarity (Sattva)
Precaution: If you have eye problems before practicing Trataka consult your eye doctor.
Featured Image Credit: AI-generated image created with Google Gemini, February 10, 2026

Basti is Traditional yogic enema is similar to Ayurvedic Basti therapy. It cleanses the intestine region.
What it cleanses?
Benefits
Ayurvedic effect: In Ayurveda, medicated basti is considered the most powerful Vata therapy.
Featured Image Credit: AI-generated image created with Google Gemini, February 10, 2026
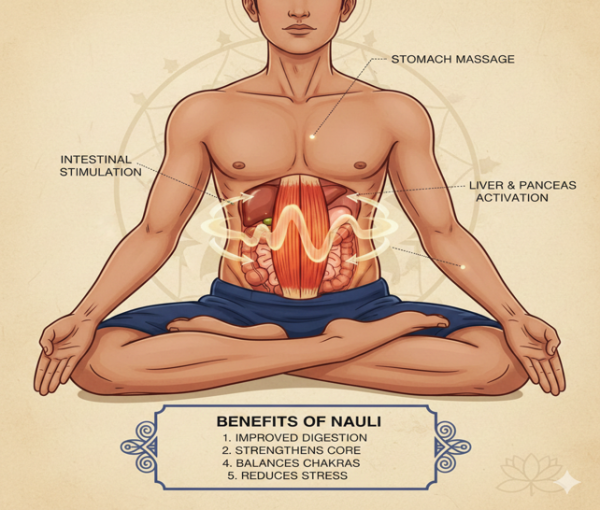
Rolling abdominal muscles while breath is held out is known as Nauli. This technique needs lots of practice. Once learnt, this is extremely helpful for cleansing abdomen regions.
What it cleanses?
Benefits
Ayurvedic effect: Balances Vata in colon, boosts Agni.
Precaution: Nauli needs lot of practice. Initially it must be supervised by an expert who knows and understands what Nauli means.
Featured Image Credit: AI-generated image created with Google Gemini, February 10, 2026