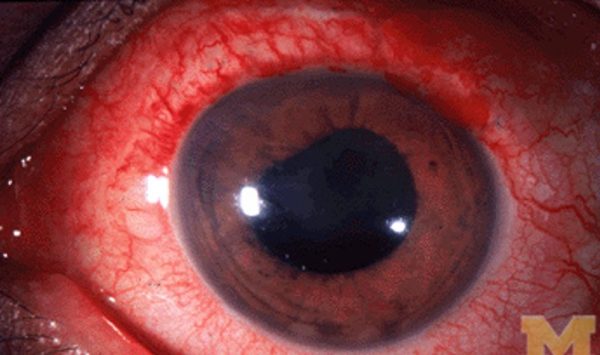
Uveitis
Uveitis is inflammation of the uvea, which is made up of the iris, ciliary body and choroid. Together, these form the middle layer of the eye between the retina and the sclera (white of the eye). Causes of uveitis include trauma or injury to the eye, infections, or rheumatologic or inflammatory diseases that affect other parts of the body. Uveitis may be associated with:
- A virus, such as shingles, mumps or herpes simplex;
- Systemic inflammatory diseases;
- A result of injury to the eye; or
- Rarely, a fungus, such as histoplasmosis or a parasite, such as toxoplasmosis.
The main symptom of uveitis is pain in the eyeball. The eye will look red (bloodshot) and you may notice blurred vision, light sensitivity, and spots in your vision.
Treatment: Treatment for uveitis depends on the cause. Uveitis is a serious eye condition that may scar the eye. It needs to be treated as soon as possible. Eye drops, especially corticosteroids and pupil dilators, can reduce inflammation and pain. If it is not treated, it may result in glaucoma, cataract, damage of retina and neovascularization.
Image credit: http://kellogg.umich.edu/theeyeshaveit/redeye/anterior_uveitis.html (CC by 3.0)
Author: Sumana Rao | Posted on: January 13, 2022






















Write a comment