
Blood Safety – Blood Donations Are Screened For Infectious Diseases
Blood donation organizations and blood banks have specific protocols and tests in place to ensure that donated blood is safe for recipients. Generally, every unit of blood is tested to identify the donor’s blood group (O, A, B or AB) and Rh type, and screened for atypical or unusual red cell antibodies. There are a few more tests that are carried out to make sure that donated blood is safe to transfer. These tests are essential for identifying potential infections and diseases that could be transmitted through blood transfusions.
While the exact tests may vary by location and organization, here are some common tests conducted to qualify blood donors for multiple diseases:
1. HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)
2. Hepatitis B and C
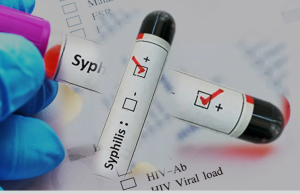
3. Syphilis
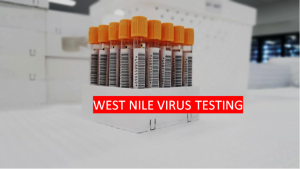
4. West Nile Virus
5. Chagas Disease.
6. Malaria
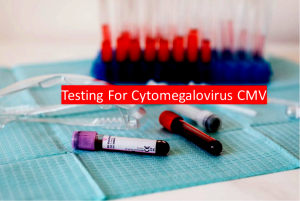
7. Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
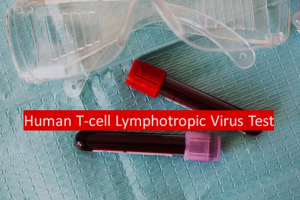
8. HTLV (Human T-cell Lymphotropic Virus)
9. Zika Virus
10. Bacterial Contamination
It’s important to note that blood banks and donation organizations have strict guidelines and eligibility criteria that potential donors must meet. These criteria include factors such as recent travel history, medical conditions, and other potential risk factors for disease transmission. Donors who do not meet these criteria or who test positive for certain infections are typically deferred from donating blood to protect the safety of both donors and recipients.
References:
https://www.redcrossblood.org/
Blood Safety Basics | CDC
Image credit: https://pxhere.com/en/photo/1649335 (CC by 0)
Testing For HIV Human Immunodeficiency Virus
Hepatitis B and C Virus Testing
West Nile Virus Infection Testing
Testing For Cytomegalovirus CMV
Author: Sumana Rao | Posted on: September 7, 2023
« Wall Push-Ups Pilates Testing For HIV Human Immunodeficiency Virus »






















Write a comment