
All You Need To Know About Refrigerated Cooked Rice And How It Benefits Health
It is still practice today that eating the previous day’s cooked rice is next day’s breakfast item. In Asian countries, rice is a staple food and rice that is left over from previous day will be used to make different items like lemon rice, porridge, curd rice etc. It is also a belief that eating the previous day’s rice gives strength! Do you know? Recent research also supports this concept. Studies show that refrigerated cooked rice from the previous day typically has a lower glycemic index (GI) compared to freshly cooked rice. This is due to the formation of Resistant Starch during the cooling process.
- Formation of resistant starch: When rice is cooked and then cooled, some of the starches retrograde into a form that resists digestion. Resistant starch slows down the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream, leading to a lower glycemic response.
- Reheating does not reverse It: Even if you reheat the cooled rice, the resistant starch remains intact, meaning the GI stays lower than freshly cooked rice.
This method of cooking, cooling, and consuming rice is often recommended for managing blood sugar levels or weight, as the resistant starch acts like dietary fiber, aiding digestion and improving satiety.
Several studies have investigated the impact of cooling cooked rice on its glycemic index (GI). The process of cooling cooked rice increases its resistant starch content, which in turn lowers its GI. This means that consuming cooled or cooled-and-reheated rice results in a slower rise in blood sugar levels compared to freshly cooked rice.
References:
- Higgins, J. A. (2004). Resistant starch and energy balance: impact on weight loss and maintenance. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.
- Ranawana, V., et al. (2009). Post-cooling of rice reduces the glycaemic response in healthy adults. Nutrition Bulletin.
- Sajilata, M. G., et al. (2006). Resistant starch–a review. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety.
Image credit: www.Healthylife.werindia.com (Copyright reserved)

How Refrigerating And Reheating Affects Rice
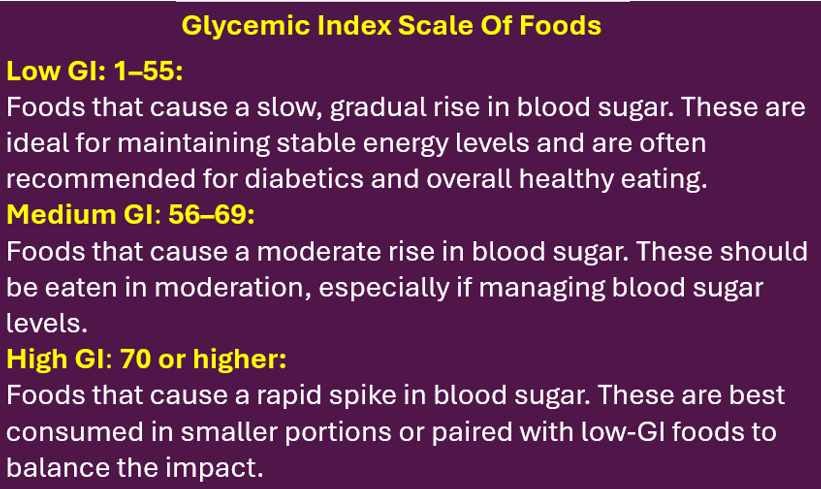
The Glycemic Index of Cooked And Refrigerated Rice

Glycemic Index Of Cooked Rice Varieties
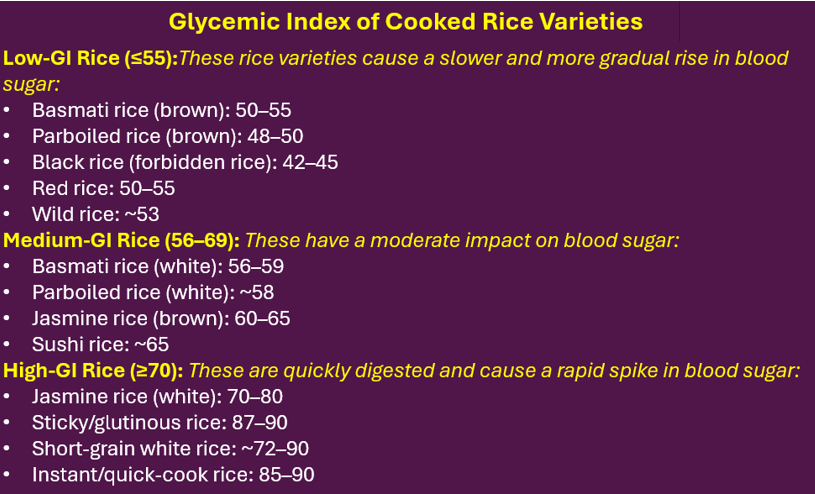

Low-Glycemic Index Strategies With Rice Eating

Practical Tips For Resistant Starch

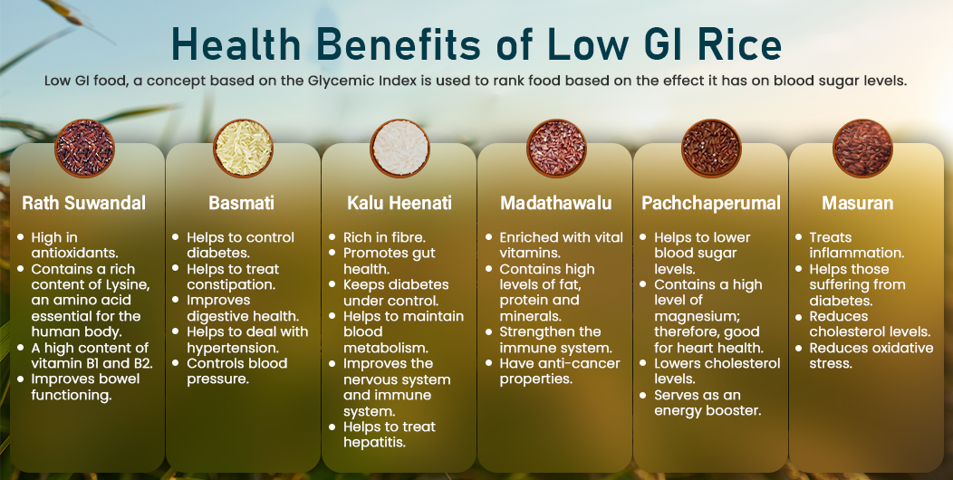
Benefits Of Eating Refrigerated Rice
Author: Sumana Rao | Posted on: January 27, 2025
« Daily Natural Tips For Lowering HbA1c Level How Resistant Starch Works »






















Write a comment