Genetically Engineered Foods Why the Controversy?
Before reading the article published in RealTruth.org understand what are genetically engineered foods?
Genetically engineered foods have had foreign genes (genes from other plants or animals) inserted into their genetic codes. Genetic engineering can be done with plants, animals, or microorganisms. Historically, farmers bred plants and animals for thousands of years to produce the desired traits. For example, they produced dogs ranging from poodles to Great Danes, and roses from sweet-smelling miniatures to today’s long-lasting, but scent-free reds.
Selective breeding over time created these wide variations, but the process depended on nature to produce the desired gene. Humans then chose to mate individual animals or plants that carried the particular gene in order to make the desired characteristics more common or more pronounced. Genetic engineering allows scientists to speed this process up by moving desired genes from one plant into another — or even from an animal to a plant or vice versa.
Function
- Potential benefits of genetically engineered food include:
- More nutritious food
- Tastier food
- Disease- and drought-resistant plants that require fewer environmental resources (water, fertilizer )
- Decreased use of pesticides
- Increased supply of food with reduced cost and longer shelf life
- Faster growing plants and animals
- Food with more desirable traits, such as potatoes that absorb less fat when fried
- Medicinal foods that could be used as vaccines or other medications
Potential risks include:
- Modified plants or animals may have genetic changes that are unexpected and harmful.
- Modified organisms may interbreed with natural organisms and out-compete them, leading to extinction of the original organism or to other unpredictable environmental effects.
- Plants may be less resistant to some pests and more susceptible to others.
Food Sources
- Tomatoes, potatoes, squash, corn, and soybeans have been genetically altered through biotechnology. Many more foods have engineered ingredients and more are being developed.
Then what is the controversy?
Experts from the article:
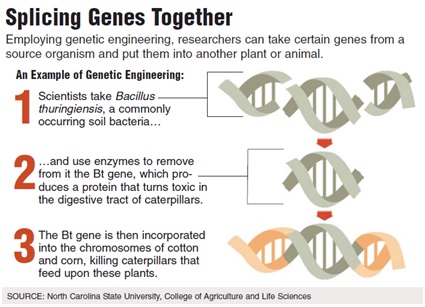
Genetic engineering (GE) is the practice of altering that genetic blueprint, to create “genetically altered” (GA) or “genetically modified” (GM) foods, or “genetically modified organisms” (GMOs). Through genetic engineering, scientists can impart desired genetic characteristics by splicing genetic segments of one species into the genes of another. This could never occur naturally. Consider one example: Certain genes from a flounder—a fish—have been inserted into tomatoes in order to give them a longer shelf life.
More details : http://realtruth.org/articles/223-gefwtc.html
Image credit: North Carolina University, College of Agriculture and Life Sciences
Author: HealthyLife | Posted on: March 24, 2015
« Political corruption of Monsanto and its influence Saving the Planet, One Meal at a Time »






















Write a comment