Bone Density Test
A bone density test—also referred to as a DXA scan or a bone mineral density (BMD) test—is the current way to diagnose osteoporosis.
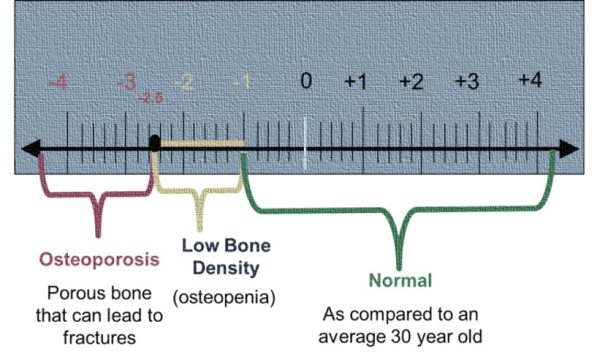
A bone density test determines if you have osteoporosis — the disease that causes bones to become more fragile and more likely to break.
The test measures the QUANTITY of bone at specific locations in the body, namely the mid-spine bones (lumbar region) and the upper end of the thighbone where it connects to the pelvis (total hip and its subdivisions – the femoral neck and trochanter).
Doctors use bone density testing to:
- Identify decreases in bone density before you break a bone
- Determine your risk of broken bones (fractures)
- Confirm a diagnosis of osteoporosis
- Monitor osteoporosis treatment
These locations are used for two primary reasons:
1) they have a large quantity of trabecular bone – the spongy, lattice-like bone on the inside- that tends to lose density as we age; and
2) measurements taken at these locations can be easily replicated so that we can determine if there are changes in the quantity (density) of bone over time.
Author: Sumana Rao | Posted on: April 22, 2022
« Make Healthy Food Choices How To Boost Your Bone Health According To Your Age Group? »




















Write a comment