Back to homepage
Human Body
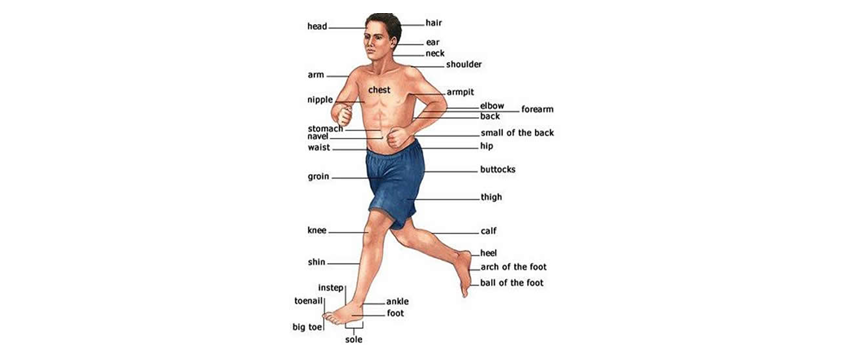
The average height of an adult human is about 5 to 6 feet tall. Human body is made up of a head, neck, torso, two arms and two legs. The human body is made to stand straight, walk on two feet, use the arms to carry and lift, and has opposable thumbs that helps to grasp.
- Hair: grown on top of the head.
- Head: part of the body that’s on top of your neck
- Eyes: for vision
- Nose: for smell
- Mouth: for eating
- Cheek: on both sides of face
- Ears: on each side of the head and used for hearing.
- Neck: connects the head to the body.
- Shoulder: connects the arm and the base of the neck
- Arms: Used for touching, eating, working etc.
- Chest: is below the neck and above the stomach.
- Arm pit: joint where the arm connects to the shoulder
- Breast: The breast is the upper front region of the chest in left and right sides, containing the mammary gland which in a female can secret milk used to feed infants
- Stomach: is used for digesting food.
- Navel: is a scar on the abdomen at the attachment site of the umbilical
- Waist: Part of the body just above hips.
- Elbow: is between the forearm and the upper arm.
- Forearm: Is between the wrist and elbow.
- Fingers: Five in each hand extended from palm –thumb, index, middle, third and little fingers
- Back: is rear surface of the body from the shoulders to the hips
- Small of the back: is the lower part of the back.
- Hips: from the waist to the top of the leg.
- Groin: above the thigh on either side of the body found in junction of the torso with the legs
- Buttocks: Sometimes called bottom or behind.
- Heel: is the back part of the foot below the ankle.
- Arch of foot: where the bottom of the foot curves.
- Ball of foot: The padded portion of the sole of the human foot between the toes and the arch.
- Instep: The padded portion foot between the toes and the arch
- Toe nails: covers the end of the top of the toes.
- Ankle: connects the foot to the leg
- Foot: the lower part of the leg below the ankle
- Big toe: each foot has 2 big toes
- Thigh: part of the leg between the hip and the knee
- Knee: connects the lower and upper leg.
- Calf: muscle at the back of the lower leg
- Shin: front of the leg below the knee
Human body comprises many systems
- Circulatory System (heart, blood, vessels)
- Respiratory System (nose, trachea, lungs)
- Immune System (many types of protein, cells, organs, tissues)
- Skeletal System (bones)
- Excretory System (lungs, large intestine, kidneys)
- Urinary System (bladder, kidneys)
- Muscular System (muscles)
- Endocrine System (glands)
- Digestive System (mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines)
- Nervous System (brain, spinal cord, nerves)
- Reproductive System (male and female reproductive organs)
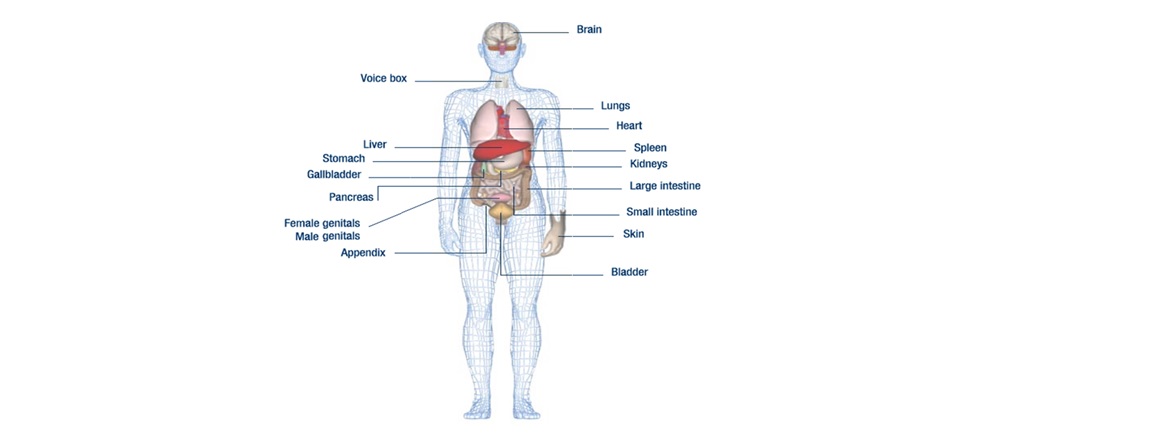
List of 10 Essential Organs of the Human Body
written by: Janelle Martel • edited by: Sarah Malburg • updated: 10/17/2014
- Skin : The skin is the largest organ in the human body. Its main job is to maintain the body’s temperature, which means that sweat is created to cool the body, and goose bumps or raised hair occur to trap heat in the body. Along with sweat glands, the skin contains oil glands. The oil your skin releases helps to keep your skin from drying out and your hair from becoming brittle. The skin also regularly sheds cells to maintain its effectiveness. If you can imagine, there are about 19 million skin cells in every square inch of the human body!
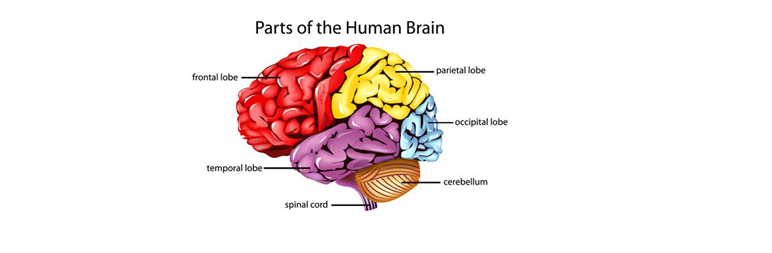
- Brain : The brain is the controller of your body, and stores information, allows you to think and learn, as well as controls vital daily functions, like digestion, heart rate, and breathing. The nervous system makes decision for our body and delivers order to the communication centre. The central nervous system (CNS) is a huge network of nerves which is made of brain and the spinal cord and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) . It has various parts like Cerebrum ,Cerebellum, Limbic System and Brain Stem. The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain which coordinates actions and thoughts. Cerebellum is the little brain which is responsible for the regulation, movement and posture. Limbic system is the emotion brain which controls all the emotions of human body.
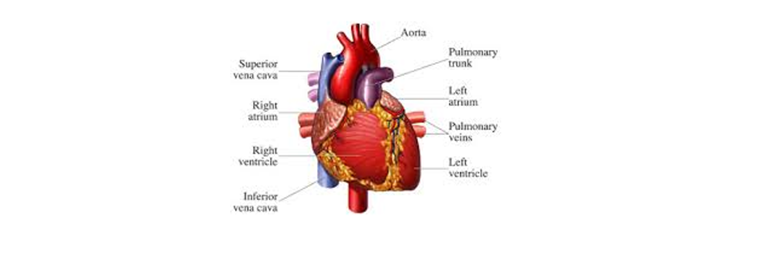
- Heart : The heart is another vital organ. The heart’s job is to pump oxygenated blood throughout your body and receive deoxygenated blood back in return. Without your heart, your other organs would not receive oxygen or have carbon dioxide removed. In an average lifetime, the heart beats more than 2.5 million times!The average human heart, beating at 72 beats per minute. The blood pumped by heart reaches all the body organs. If the heart stops pumping then the whole body mechanism will fail and thus it will lead to death. But now a days when heart fails there are heart transplant.
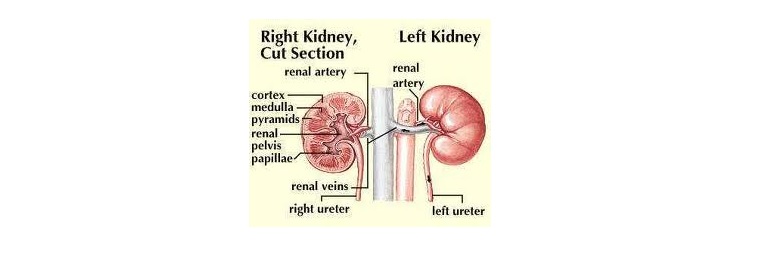
- Kidneys : Did you know that a healthy person is able to live with only kidney? he kidneys are located under the ribcage in your lower back. The job of the kidneys is to filter things like water and salts out of your blood and to produce urine. The kidneys also produce an enzyme called rennin. This enzyme plays a big role in regulating your blood pressure. Most people know that a major function of the kidneys is to remove waste products and excess fluid from the body. These waste products and excess fluid are removed through the urine. Kidneys are known as powerful factories which perform various functions and those functions say about its importance. Kidney removes the drugs from the body and balances the body fluids. It also releases the hormones which are necessary for controlling the blood pressure. One of the most important functions is controlling production of red blood cells along with vitamin D to keep bones strong and healthy. Kidney diseases are widespread diseases. When the kidneys stop working completely, the patient needs a kidney transplant or dialysis treatment to keep them alive. When the person becomes diseased the person becomes more and more ill as toxins gets accumulated in the body.
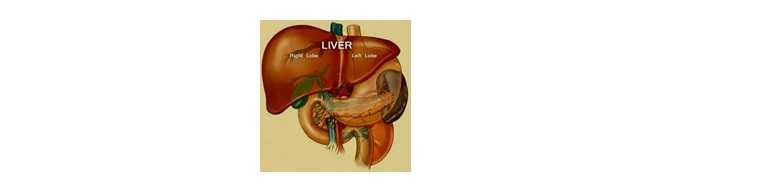
- Liver : The liver is located in the upper abdomen, slightly more to the left side. Liver is one of the most important organ and the largest gland of the body weighing 1.5 kg.It is located in the central position of the abdomen. It receives 30 % of the blood every minute. It has importance which is crucial to one’s life like storing of vitamins, sugar and iron to give body energy, controlling the production and removal of cholesterol, clearing the blood of waste products, drugs, and other poisonous substances. It also releases and important substance called “bile “which is necessary to digest food and absorb nutrients. The liver is such an important organ that we can survive only one or two days but if it fails the whole system and thus body fails. It also helps in the synthesis of plasma proteins such as albumin andclotting factors and purification of the body.
- Large Intestine : The large intestine is located in your abdomen and is 1.5 meters in length! The large intestine is involved in digestion, and receives undigested food from the small intenstine. The large intestine then absorbs as much water as possible and then expels the waste and any excess fiber.
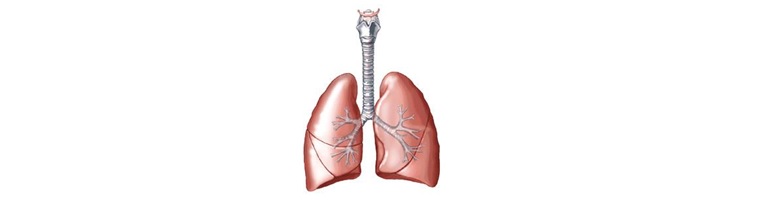
- Lungs : The lungs are located in your chest and are protected by your rib cage. The lungs take in oxygen which goes into the blood through the heart, and expels carbon dioxide as the heart receives unoxygenated blood.Lungs are an important organ without which life is totally impossible . Your lungs are part of a group of organs and tissues that all work together to help you breathe. This system is called the respiratory system. The right lung is slightly larger than left lung and the surface area of lungs is same like the surface area of tennis court. History emphasized their importance as cooling agents that maintained the balance of the human body by counteracting the hot temperament of the heart.
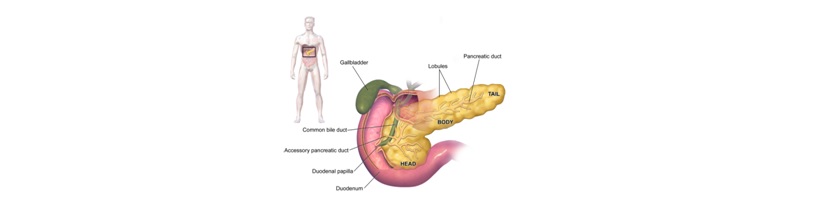
- Pancreas : The pancreas is located in the abdomen, behind the stomach. The job of the pancreas is to produce enzymes necessary for digestion and send them to the stomach. The pancreas also regulates blood sugar and does this through its process of creating insulin. The pancreasalso creates glucagon which has the opposite effect of insulin and also helps to maintain blood sugar levels.
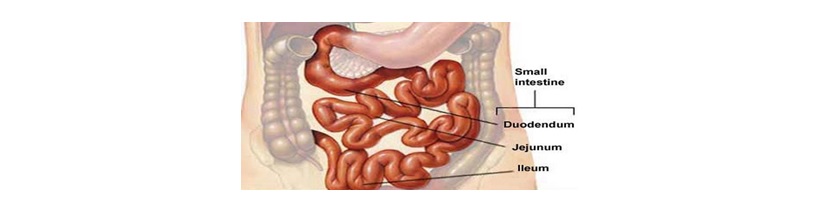
- Small Intestine : The job of the small intestine is to digest food. It does this using chemicals, such as enzymes. The small intestine also absorbs nutrients from the food through villi and gives these nutrients to your blood. The small intestine (small bowel) is about 20 feet long and about an inch in diameter. Its job is to absorb most of the nutrients from what we eat and drink. Velvety tissue lines the small intestine, which is divided into the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
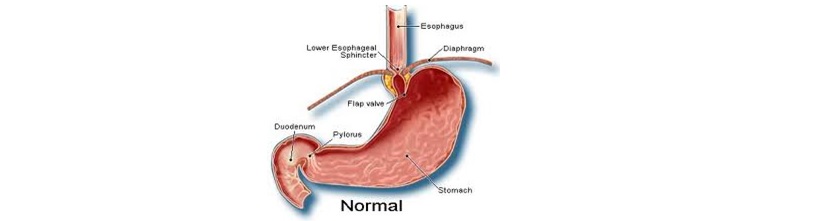
- Stomach : Whatever we eat or drink it goes inside our stomach whether its water, vegetables, milk etc. When we eat it increases the surface area. The stomach is a muscular organ located on the left side of the upper abdomen. The stomach receives food from the esophagus. As food reaches the end of the esophagus, it enters the stomach through a muscular valve called the lower esophageal sphincter. The stomach secretes acid and enzymes that digest food. Ridges of muscle tissue called rugae line the stomach. The stomach muscles contract periodically, churning food to enhance digestion. The pyloric sphincter is a muscular valve that opens to allow food to pass from the stomach to the small intestine.