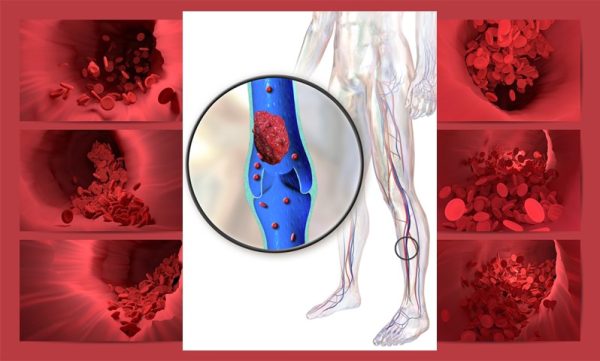
Blood Clot– Preventive Measures
Are you a frequent long distance traveler? Do you have an upcoming surgery or have you undergone surgery recently? Then, you should be knowing risk of blood clot in your system. Blood clotting is very risky condition but can be preventable. In medical terms it is known as deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism or commonly called Venous thromboembolism (VTE).
What you need to know about blood clot to protect yourself
Anyone can be at risk for blood clots, also known by the medical term venous thromboembolism (VTE). VTE is a serious and growing public health concern, occurring either as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE).
DVT occurs when blood clots form in the deep veins of the body, usually the lower leg, thigh, or pelvis, but they can also occur in other areas of the body such as the abdomen and arms. PE occurs when a blood clot breaks off and travels through the bloodstream to the lungs. PE can be deadly.
It is important to learn about VTE so that you can protect yourself.
Key Facts:
Anyone can develop a blood clot. In the United States, as many as 900,000 people are affected by VTE each year and about 100,000 people die of PE annually.
Many factors can put you at risk for a blood clot. These include:
• having a major trauma
• having cancer
• being age 55 and older
• having a personal or family history of blood clots
• being immobile (such as being on bed rest or difficulty with walking)
• pregnancy, or using estrogen containing medications such as birth control pills, patches, and hormone replacement therapy
• being obese
Almost half of all blood clots occur either during or soon after discharge from a hospital stay or following a surgery. The more risk factors you have, the greater will be your risk of developing a blood clot.
Signs and Symptoms of DVT
About half of people with DVT have no symptoms at all. The following are the most common symptoms of DVT that occur in the affected part of the body:
• Swelling
• Pain
• Tenderness
• Redness of the skin
If you have any of these symptoms, see a professional as soon as possible.
Signs and Symptoms of PE:
You can have a PE without any symptoms of a DVT. Signs and symptoms of PE can include:
• Faster than normal or irregular heartbeat
• Chest pain or discomfort, which usually worsens with a deep breath or coughing
• Coughing up blood
• Very low blood pressure, lightheadedness, or fainting If you have any of these symptoms, seek medical help immediately.
Get Informed and Learn How to Protect Yourself
• Talk to your family to see if you have, or have had, any family members with blood clots. Share this family history with your healthcare professional.
• Know your risks and recognize the signs and symptoms. If you have any symptoms, see your healthcare professional as soon as possible. Blood clots can be safely treated.
• If you are admitted to a hospital, or are planning to have surgery, ask your healthcare professional “What is my risk of developing a blood clot?” and ask for a risk assessment (a tool that healthcare professionals use to help determine your risk of developing a blood clot). Ask your healthcare professional
if you should receive preventive measures to protect you from having a blood clot.
• When sitting for long periods of time, such as when traveling for more than four hours, there are things you can do to improve the flow of blood in your legs.
» Move your legs frequently when on long trips or while sitting for long periods of time, and exercise your calf muscles to improve the flow of blood. Take a break to stretch your legs.
Extend your legs straight out and flex your ankles, pulling your toes toward you.
» When driving, stop the car every two hours and walk for a few minutes. While flying, when it is safe to do so, get up every hour and walk the length of the airplane cabin a few times.
Prevention is Key
There are proven ways to prevent blood clots from occurring, such as compression devices while in the hospital or blood thinning medicines called anticoagulants to prevent or treat blood clots.
Talk with your healthcare professional to learn more about the risks for blood clots and how to prevent them.
For more information on blood clot prevention please visit https://www.cdc.gov/
Image credit: BruceBlaus. Blausen.com staff (2014). “Medical gallery of Blausen Medical 2014”. WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (2). DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 2002-4436., CC BY 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
Imagen de Narupon Promvichai en Pixabay (cc by 0)
Author: HealthyLife | Posted on: May 31, 2023






















Write a comment