Chronic Pain and Relief
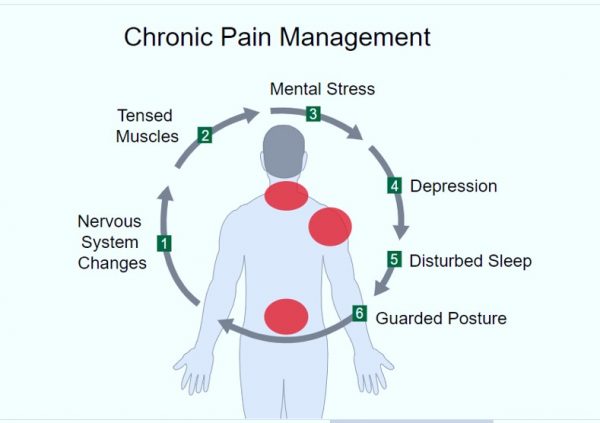
There are few things more frustrating to a person with chronic pain than hearing someone say, “Your pain is all in your mind.” Chronic pain is in the mind—but this does not mean what you think it means. The experience of pain is real. Pain has a biological basis. Many aches and pains are rooted in brain processes that can be affected by your mental attitude and emotions. The mind, emotions and attention play an important role in the experience of pain. Chronic pain is not the same as the pain you feel from an injury. That is acute pain—the sensing of tissue damage by nerves. In people with chronic pain, stress, fear and depression can amplify the perception of pain.
Our brain, and consequently your thoughts and emotions, do play a role in your experience of physical pain. For instance, meditation appears to work for pain relief because it reduces brain activity in your primary somatosensory cortex, an area that helps create the feeling of where and how intense a painful stimulus is. Laughter is also known to relieve pain because it releases endorphins that activate brain receptors that produce pain-killing and euphoria-producing effects. Following natural treatments can help people to get relief from chronic pain.
Acupuncture
One of the main uses of acupuncture is for pain relief. Acupuncture is also thought to decrease pain by increasing the release of chemicals that block pain, called endorphins. Acupuncture may be useful as an accompanying treatment for many pain-related conditions, including headache, low back pain, menstrual cramps, carpal tunnel syndrome, tennis elbow, fibromyalgia, osteoarthritis and myofascial pain.
Chiropratic treatment
Chiropractic treatment is the most common non-surgical treatment for back pain. Improvements in people undergoing chiropractic manipulations were noted in some trials. Research also suggests that chiropractic treatments may be helpful for headaches, neck pain, certain arm and leg conditions, and whiplash.
Massage:
People suffering from pain, mostly to manage chronic back and neck problems, are increasingly using massage. Massage can reduce stress and relieve tension by enhancing blood flow. This treatment also can reduce the presence of substances that may generate and sustain pain.
Dietary Approaches for treating Pain
Some people believe that changing dietary fat intake or consuming plant foods that contain anti-inflammatory agents can help ease pain by limiting inflammation. A mostly raw vegetarian diet was found helpful for some people with fibromyalgia. In fact, satvik food which does not have too much spice, no meat can help people to get rid of those pains. Increasing consumption of fruits also helpful. One study of women with premenstrual symptoms suggested that a low-fat vegetarian diet was associated with decreased pain intensity and duration. Weight loss achieved by a combination of dietary changes and increased physical activity has been shown to be helpful for people suffering from osteoarthritis.
Meditation:
Research has shown that chronic pain is associated with distress and that meditation has stress relieving benefits. MIT and Harvard neuroscientists found that people trained to meditate are better able to control “alpha rhythms” brain waves, thought to be responsible for minimizing distractions. After learning how to meditate, research participants’ alpha waves were significantly amplified when focusing on specific body parts. The findings suggest that those who suffer chronic pain—including stress—may benefit from meditation because of an increased ability to “turn down the volume on pain signals.” If you have chronic pain or stress, mindfulness-based stress reduction or meditation may help you ease that pain. It has also been suggested that meditation can actually exercise brain’s “muscles” to increase focus, and has been shown to lower stress and increase forgiveness which means bringing stress level way down.
Herbal Remedies
Though research on herbal remedies is still in its early phases, many herbs are thought to provide pain management and decrease inflammation. However, it is important to exercise caution.
Here are some common herbal remedies used for natural pain relief:
Capsaicin: Derived from hot chile peppers, topical capsaicin may be useful for some people in relieving pain. Capsaicin works by depleting substance P, a compound that conveys the pain sensation from the peripheral to the central nervous system. It takes a couple of days for this to occur.
Pepper: Raw pepper is helpful in controlling headaches. Paste of raw black pepper can be applied on both sides of forehead to reduce stress pain.
Ginger: Ginger extract may help with joint and muscle pain because it contains phytochemicals, which help stop inflammation. Few side effects have been linked to ginger when taken in small doses. Ginger reduces inflammation of stomach and releases pain.
Turmeric :This Indian spice has been used to relieve arthritis pain and heartburn, and to reduce inflammation. Its activity is due to a chemical called curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory properties. Turmeric is usually safe to use, but high doses or long-term use may cause indigestion. Little turmeric, black pepper powder and honey can do wonders on pain relief.
Khashaya: Crushed cumin and coriander seeds, ginger and black pepper boiled in hot water is called Khashayam. One can have the dicoction with milk and sugar. This also relieves body pain.
Ginseng tea: The health benefits of ginseng tea include a number of curative and healing properties. The tea is derived from a perennial plant root. Ginseng tea reduces physical and mental distress, and has a relaxing and soothing effect on the body.
Disclaimer: This article is for educational purpose. If you have any chronic pain please contact your physician before beginning any such therapy.
References:
Image credit:https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Chronic_Disease_Pathways.svg, Attribution Akiyao from the University of Michigan Medical School / CC BY-SA (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)
Author: Sumana Rao | Posted on: August 31, 2015
« Remedies for Poor Eye Sight Detrimental effects of Junk Food on children »






















Write a comment