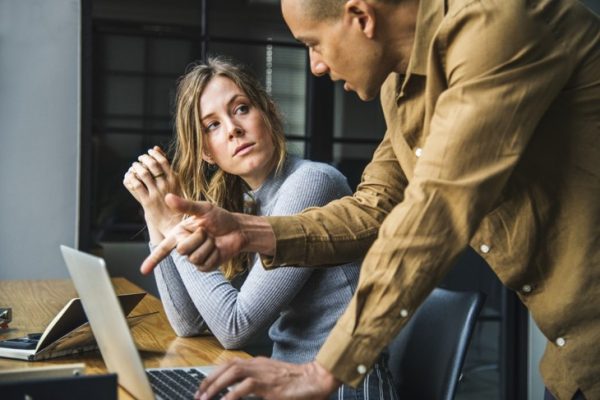

Understanding And Addressing Passive Aggressive Behavior
Passive-aggressive behavior is a pattern of indirectly expressing negative feelings instead of openly addressing them. The main characteristic of this behavior is a disconnect between what the person says and what they do. Instead of communicating honestly and directly, someone acting passive-aggressively might use sarcasm, silent treatment, subtle insults, or deliberate procrastination to express resentment, anger, or displeasure. This behavior can stem from an inability or unwillingness to confront feelings or handle conflict directly.
Characteristics of Passive-Aggressive behavior
- Procrastination: Delaying tasks, especially those important to someone else, as a form of indirect resistance to demands or expectations.
- Sullenness: Displaying silent resentment and a gloomy attitude instead of openly expressing dissatisfaction.
- Silent Treatment: Ignoring someone or refusing to speak to them as a way of expressing anger or annoyance without verbal confrontation.
- Subtle Sabotage: Intentionally making mistakes or obstructing projects or tasks to undermine others.
- Backhanded compliments: Giving compliments that contain a critical or negative observation, often used to demean or undercut someone subtly.
- Sarcasm and cynical comments: Using sarcasm or cynicism to express contempt or ridicule indirectly.
- Denial: Denying feelings of anger, resentment, or dissatisfaction when they are apparent to others, often accompanied by phrases like “I am fine” or “Nothing is wrong” when it is clear that is not the case.
- Avoiding responsibility: Using excuses to avoid taking responsibility for one’s behavior or tasks, often in a way that places the blame on circumstances or other people.
Causes: Passive-aggressive behavior can be a response to situations where the individual feels powerless or lacks the skills to express their emotions constructively. It might be rooted in upbringing, particularly in environments where open expression of emotions was discouraged or punished. It can also develop in environments (like overly restrictive workplaces or relationships) where direct communication is not safe or welcome.
Impact: Passive-aggressive behavior can be frustrating and damaging to relationships, whether personal or professional. It can lead to misunderstandings, conflict, and a breakdown in communication. Over time, it erodes trust and respect between people, making it difficult to build healthy, functional relationships.
Addressing Passive-Aggressive behavior
- Self-Reflection: Individuals exhibiting passive-aggressive behavior should reflect on their actions and consider the underlying feelings driving their behavior.
- Communication skills: Learning and practicing assertive communication can help individuals express their thoughts and feelings directly and constructively.
- Seek support: Therapy or counseling can provide a safe space to explore the reasons behind passive-aggressive behavior and develop healthier coping strategies.
- For receivers: If you’re on the receiving end, addressing the behavior directly and calmly with the person, focusing on how their actions affect you, can sometimes help. However, it is important to set boundaries and not engage in retaliatory passive-aggressive behavior. (We will talk about how to respond to passive aggressive behavior in our next Mind and Body article).
Understanding and addressing passive-aggressive behavior is crucial for fostering healthier, more honest, and constructive interactions in both personal and professional settings.
Image credit: Pxhere : rawpixel.com (CC0 Public Domain)
Author: Sumana Rao | Posted on: March 26, 2024
« Benefits Of Practicing Advanced Bird Of Paradise Pose Svarga Dvijasana How To Respond To A Person With Passive Aggressive Behavior »





















Write a comment