
February 27, 2023
Author: HealthyLife | Posted on: February 27, 2023







Kuldhas are clay cups also known as desi cups used for drinking both hot and cold drinks like tea, coffee, lassi or can be used for ice cream. It can be recycled, reused or if thrown it will mix with earth. Now, instead of clay cup, Indian farmers used edible millet to make these kulhads. After drinking instead of throwing the cups one can eat the cup just like a snack.
Why millet? Millets are recognized for their low glycemic index and for providing all good health benefits. Year 2023 is declared as International year of millets by UN following India’s proposal. Millets are environmentally friendly and are affordable. Eating millet khudlha is a great initiative to promote healthy millets eating – Healthy Life
There are millions who enjoy eating ice creams from cones and then munching on the cones too. A Deoria-based farmers’ group in Uttar Pradesh has now come up with ‘kulhads’ made from millet that can be used to drink tea and then eaten as a healthy snack.
Interestingly, these ‘kulhads’ come at a time when 2023 has been declared as the “International Year of Millets” by the United Nations after a proposal from India in 2019.
Christened ‘Chai Piyo aur Kulhad Khao’, these nutritious kulhads, made of co-arse grain of ragi and maize flour, have caught the attention of tea lovers at the ongoing Magh Mela in Prayagraj.
Ankit Rai, a member of the group, said the demand for these ‘kulhads’ has been increasing manifold in rural as well as urban areas of eastern Uttar Pradesh.
He said, “To promote the benefits of millets, we created edible kulhads made of millets about two years ago. We have a special mould wherein we can make 24 cups in one go.”
“Initially, we connected with tea vendors in small villages of east UP, including Deoria, Gorakhpur, Siddharth Nagar and Kushinagar, but we managed to win hearts in other parts as well. Now, the demand has spread to Prayagraj, Varanasi, Lucknow and other districts.”
Talking about the price of these ‘kulhads’, he said, “It takes Rs 5 to shape such kulhads and when tea is served in it, it costs Rs 10. The ‘kulhads’ are also eco-friendly. They are in line with Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s Swachh Bharat Mission as there is zero wastage.”
Women are mostly involved in making ‘kulhads’ of millet for health benefits.
Syndicated article from IANS
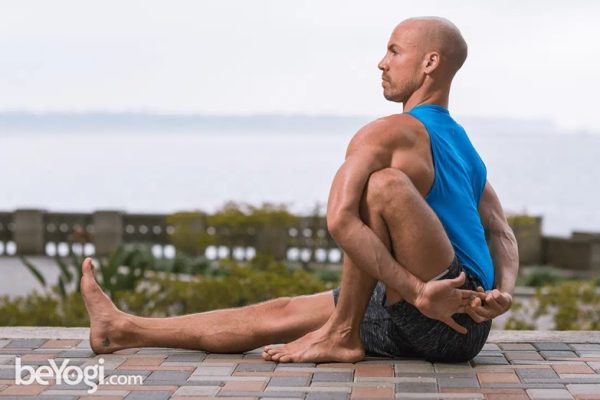

Marichyasana is one legged seating pose where yogi will sit on floor by extending one leg and with spinal twist. It is an intermediate level yoga pose. Pose dedicated to great sage Marichi who is one of the seven sages (saptarishis). Marichi means “ray of light”. Sage Marichi is the founder and originator of Hindu Vedanta. Apart from calming the mind, pose helps to tone the body and activates digestive system – Healthy Life
LEVEL: Beginner
Anatomy: Digestive System, Shoulders, Spine
Pose Type :Forward Bend, Hip Opener, Seated
Sanskrit :Marichyasana (mar-ee-chee-AHS-anna) Marichi = a sage; son of the creator Brahma
BENEFITS :
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
HOW TO:
MODIFY OR REPLACE:
Alternatives:
Modifications:
SEQUENCING TIPS:
Before:
After:
TEACHING CUES:
VARIATIONS:
WATCH OUT FOR:
Article and image published here with prior permission from beyogi.com