Health Tips To Overcome Overactive Bladder Condition
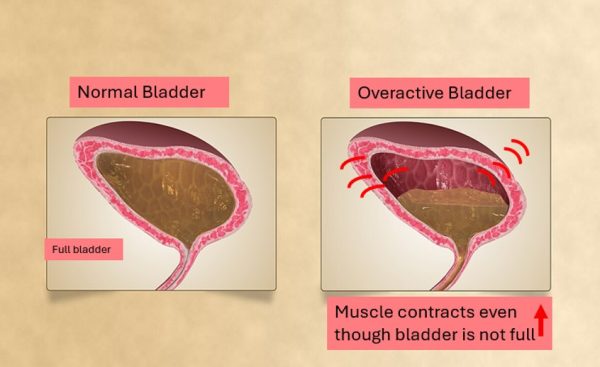
If you are dealing with an overactive bladder (OAB), several home remedies and lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms naturally. OAB happens when the bladder muscles contract involuntarily, even when it is not full, causing frequent urges to urinate. As we age this condition can cause more issues. Sensitive bladder squeezes to pass urine without our consent. OAB effect both men and women.
Symptoms: OAB does not cause pain.
- Passing urine frequently – while at home, night times (nocturia), while at work or during exercise.
- Some people have leak, and some may suddenly develop feeling of “got to go” now.
- Feeling that you must pass urine.
Apart from age factors, other factors can contribute to this condition:
1. Nerve and muscle dysfunction:
- Neurological conditions – Diseases like Parkinson’s, multiple sclerosis (MS), or stroke can disrupt nerve signals to the bladder.
- Weak or overactive bladder muscles – The detrusor muscle (which controls urination) may contract too often or too strongly.
2. Hormonal changes:
- Menopause and estrogen decline – In women, lower estrogen levels can weaken bladder tissues.
- Pregnancy and childbirth – Can stretch and weaken pelvic muscles, leading to bladder control issues.
3. Irritation and infections:
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs) – Can cause inflammation and a frequent urge to urinate.
- Bladder irritants – Caffeine, alcohol, artificial sweeteners, spicy foods, and acidic drinks can worsen symptoms.
4. Lifestyle and health conditions:
- Obesity – Excess weight puts pressure on the bladder.
- Smoking – Can lead to chronic coughing, weakening pelvic floor muscles.
- Chronic constipation – Straining weakens pelvic muscles, affecting bladder control.
5. Medications and other factors:
- Diuretics – Used for high blood pressure, these increase urine production.
- Sleep disorders – Poor sleep can make nighttime urination (nocturia) worse.
How to take care of overactive bladder?
Dietary adjustments:
- Pumpkin seeds – Pumpkin seeds are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which can help reduce inflammation in the bladder.
- Magnesium-rich foods – Bananas, spinach, and almonds may help relax bladder muscles.
- Vitamin D – Sunlight exposure or fortified foods (like plant-based milk) may improve bladder control.
- Avoid bladder irritants – Cut back on caffeine, alcohol, sugary drinks, spicy foods, and artificial sweeteners.
Hydration and bladder training:
- Timed voiding – Try urinating on a schedule (every 2-4 hours) to train your bladder.
- Double voiding – After urinating, wait a few minutes and try again to empty your bladder fully.
- Stay hydrated – Drink water consistently but avoid excessive intake before bedtime.
- Eat fiber – Consume good source of fiber every day to avoid constipation.
Herbal remedies: Ayurveda offers several herbs that may help with an overactive bladder by strengthening the urinary system, reducing inflammation, and balancing Vata dosha which is often associated with bladder issues.
- Corn silk tea – Used traditionally to soothe bladder irritation.
- Gosha-jinki-gan (GJG) – A Japanese herbal blend that may reduce urgency.
- Horsetail – Can help strengthen the bladder and reduce leaks.
- In Ayurveda, the following herbal treatments are used for overactive bladder: Gokshura, Varuna, Shatavari, Ashwagandha, Punarnava and Chandrapabha vati (multiple herbs).
Pelvic floor exercises:
- Kegel exercises – Strengthen bladder–supporting muscles to improve control.
- Yoga – Poses like “child’s pose” and “bridge” may help relax and tone the pelvic area.
Lifestyle changes:
- Regular exercise – Helps maintain a healthy weight, reducing pressure on the bladder.
- Elevate legs at night while sleeping – Helps prevent nighttime urination by redistributing fluids.
If your problem persists after 2-3 weeks, talk to your general physician and they will help you to overcome the problem through different diagnosis.
Image credit: http://www.scientificanimations.com/, CC BY-SA 4.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commonshttps://www.urologyhealth.org/
Author: Sumana Rao | Posted on: March 18, 2025
« Tooth Sensitivity, Reasons and Remedies Health Tips And Exercises To Recover From Heel Pain Plantar Fasciitis »






















Write a comment