FOOD ALLERGY: FOODS, SYMPTOMS
- The most common food allergy signs and symptoms
- Outgrowing Allergies
- Anaphylaxis: Severe Reaction
- Myth: Food Allergies Are Predictable
- Precautions and risk management for food allergies
- Which foods trigger allergies?
- How to diagnose the allergy?
- Common foods that can cause allergy
- Oral Allergy Syndrome
- Food Intolerance: What is it?
Definition for allergy is – An allergy is a false alarm triggered by the body’s immune system as a response to some substances in our environment, e.g. pollens, dust in the environment or protein in food. As a result, our bodies generate specific antibodies in response to the “foreign substances” or antigens. When the body comes into contact with these substances again, an allergic reaction such as itching, skin rash, stomach pain or breathlessness is triggered by the release of substances resulting from a reaction between the antigens and antibodies.Around 6% of children and 4% of adults suffer from this problem all over the world.
Food allergies are common among kids, and can develop suddenly. Any food can cause an allergy, but those most apt to trigger an allergic reaction are cow’s milk, eggs, peanuts, soy, wheat, nuts from trees, fish and shellfish. Kids having an allergic reaction may complain about their lips, mouth, tongue or throat — which may feel itchy, tight or funny. Young children who don’t yet speak may put their hands in their mouth and pull or scratch their tongue.
Food allergies that emerge in babies and toddlers often disappear by the time the child goes to school if they avoid having the offending foods when they are young. This happens as the food in question has not been absorbed by the body over a long period of time.
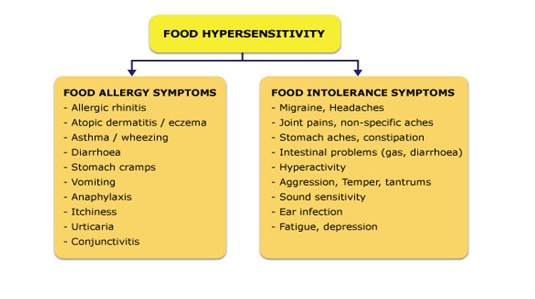
The most common food allergy signs and symptoms include :
- Tingling or itching in the mouth.
- Hives, itching or eczema.
- Swelling of the lips, face, tongue and throat or other parts of the body.
- Wheezing, nasal congestion or trouble breathing.
- Abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea or vomiting.
- Dizziness, lightheadedness or fainting.

Outgrowing Allergies
Children are likely to outgrow allergies to milk, egg, wheat, and soy. However, kids with peanut, tree nut, fish, and shellfish allergies usually have them for life. If you want to see if your child has outgrown her allergy, your doctor can do a blood test. Do not try to feed your child a food on your own to check. Even a small amount of a food can cause a life-threatening reaction.
Anaphylaxis: Severe Reaction
Symptoms can sometimes be so bad that they can be life-threatening. This is called anaphylaxis. When this happens it can tighten someone’s airways and throat so much that they can’t breathe. Their blood pressure can drop fast. If you have food allergies, your doctor may prescribe epinephrine (EpiPen) to always carry with you. Use the injection at the first sign of a reaction. Then go to an emergency room.
Myth: Food Allergies Are Predictable
One bite of seafood went down well last time. Does that mean one bite is always safe? Maybe, maybe not. In general, how much of an allergic reaction you’ll have depends on how bad your allergy is and how much of the trigger food you eat. But reactions can be unpredictable. While you may have hives one time, you could have vomiting or breathing problems next time.
Precautions and risk management for food allergies:
Allergies can be scary. Strict avoidance of a food is the only way to assure you avoid a reaction. If you feel you or your child is allergic to a certain food:
- Immediately eliminate the food from the diet and check if the reactions stop
- Confirm whether the reaction was due to allergy by taking a test
- Once you know your food allergen, check whether you should avoid any other foods that may cause allergic reaction
- Read labels while buying any processed foods. Check if the ingredients contain the allergen before consuming processed foods
- Carry your prescribed medicines wherever you go
- See a doctor for special diet
- Let your dear ones know about your food allergy
Which foods trigger allergies?
- Cow’s milk, hens’ eggs and soya in infants
- Cow’s milk, hens’ eggs, fish, soya, nuts like peanuts, tree nuts and cereals like wheat in children
- Vegetables, fruit, Spices, nuts, hens’ eggs, cow’s milk and fish in adults
Common foods such as egg, wheat, peanuts, milk and chickpeas are related to almost 90% of food allergies found in India. The incidence of these allergies varies across India depending on food consumption in different regions, religions and cultures.

How to diagnose the allergy?
To diagnose a food allergy, the first step is usually to keep a food diary. Note what your kids eat and the symptoms that follow. Next, a pediatrician will likely recommend eliminating the foods that seem to trigger the allergic reactions. Sometimes a doctor will supervise something called an oral food challenge, where the allergic person is exposed to the suspected food. Other tests may include a radioallergosorbent blood test (RAST) to check the number of antibodies produced by immune system, which can help identify specific allergens. An allergy skin test, or scratch test, may also be performed to help identify what is causing the allergic reactions.
Allergy Testing
You may be able to find out what you’re allergic to by getting tests.
- Skin prick test — An allergist puts a drop of liquid on your skin, then pricks the skin to allow it to soak in. No reaction means you’re not allergic. This is the most common allergy test.
- Blood test – By taking a sample of your blood, they can see if it reacts to certain triggers.
- Supervised food challenge – While a doctor watches, you eat foods to see if you react.

Images Courtesy : http://www.webmd.com
Common foods that can cause allergy
Some common foods that can cause allergies in children (and in adults too) are described below.
Wheat and corn allergy: (http://www.thehealthsite.com)
These allergies are common in children and adults who consume wheat and wheat products such as bread, cookies, malt products, alcoholic beverages, processed meat and seasonings. According to a report published in the Indian Journal of Medical Research (IJMR), wheat allergy is becoming more common in North India due to the varieties of wheat crops grown and the increased use of pesticides. It is found in both children and adults. If it develops during childhood, it lasts forever.
How is it recognized?
On eating anything that contains wheat and corn, if you notice the below symptoms you could be suffering from the allergy.
- Indigestion, flatulence, stomach ache and diarrhoea
- Hyperacidity and stomach ulcers
- Hyperactivity or aggressive behaviour
- Fatigue and depression
- Muscle pain and cramps
- Asthma
- Eczema
Why should you take it seriously?
Gluten allergy can cause serious allergic reactions leading to complications like chest pain and tightness, difficulty in breathing and swallowing, swelling of throat, pale skin and very low BP.
Allergy due to milk and milk products:
These allergies are common in children and adults who consume cow milk and milk products like ice-cream, lassi, buttermilk, cheese and yoghurt. In India, milk allergy is commonly found in metropolitan cities like Delhi, Bangalore, Madras and Mumbai where the use of milk powder, imported from Europe to provide reconstituted milk, and tetra pack milk or pooled milk is increasing. According to 1990 estimates, milk allergy was found in less than 5% of Indian population. But as of 2013, more than 50% of people residing in these cities now suffer allergies and health problems caused by milk and milk products.
There are more than 25 different components in milk which have been identified by researchers as potential food allergens. The protein that usually triggers an immunological reaction in milk is S1-caesin. Deterioration of milk quality is also one of the reasons why milk allergy is becoming common in India. Contamination of milk due to widespread use of chemical pesticides on cow feed has increased the chances of allergic reactions to milk.
How is it recognized?
Common symptoms include wheezing, vomiting or development of an evident red, itchy rash on skin called as hives. Other symptoms which may take a while to fully develop include:
- Diarrhea and stomach cramps
- Coughing
- Nose irritation and runny nose
- Watery eyes
- Skin rash around the mouth
- In infants, colic is commonly seen
Children and adults with milk allergy rarely develop complications. But they more likely to develop allergies to other foods such as peanuts or eggs which can lead to complications.
Egg allergy: These allergies are common in children and adults who consume eggs in any form and egg products such as cakes, pastries, baked foods, mayonnaise, pasta, soups and wine, which contain eggs. Egg allergies are most common in infants between 6 and 15 months of age. It is believed that egg whites cause more allergy than the yolks. In rare cases, people might be allergic to both.
How is it recognized?
On eating egg or products containing eggs, if you notice the following symptoms you might be suffering from allergy to eggs.
- Red bumpy rashes on the skin soon after eating eggs.
- Eczema
- Vomiting, nausea
- Stomach cramps or diarrhea.
- Asthma with coughing and wheezing.
- Respiratory symptoms include runny nose and sneezing.
- Watery and itchy eyes
Why do you need to take it more seriously?
Egg allergy can lead to serious allergic reactions (anaphylaxis). Symptoms such as severe stomach pain and cramps, increased pulse rate, dizziness or loss of consciousness can indicate a medical emergency.
Allergy due to peanuts and other tree nuts such as walnuts, almonds and cashewnuts:
Allergies are common in children and adults who consume plain roasted peanuts and products containing peanuts. About 33% of individuals who have peanut allergy may also show allergic reaction to other tree nuts. According to a report published in the Journal of the Indian Medical Association, peanuts are the most common food allergen in India. Peanut allergy is seen in both adults and children. It is observed that about 9% percent of children suffering tree nut allergy and 20% of children having peanut allergy eventually outgrow their allergy as adults.
Researchers believe that exposing peanuts to high temperature while roasting alters their protein structure which increases the likelihood of allergic reaction. Chances of peanut allergy increase in people having other forms of allergy such as asthma, eczema and hay fever.
How is it recognized?
- Skin reactions, such as hives, reddening or swelling of skin
- Itchy throat and mouth
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea, stomach cramps
- Tightening of throat
- Shortness of breath
- Runny nose
Why do you need to take it more seriously?
Peanut allergy is the most common cause of food-induced serious allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) leading to a life-threatening condition. Complications include:
- Constriction of airways
- Breathing difficulty due to swelling of throat
- A sudden drop in blood pressure
- Increased pulse rate
- Loss of consciousness
Oral Allergy Syndrome:
An allergy to fresh fruits and vegetables is called oral allergy syndrome. People who have hay fever, especially hay fever triggered by birch or ragweed pollen, are most likely to get it. Uncooked apples, cherries, kiwis, celery, tomatoes, and green peppers may cause tingling, itching or swelling of the lips, tongue or throat. They can also cause watery or itchy eyes, a runny nose, and sneezing.
Living With Food Allergies
With no cure for food allergies, you need to avoid your trigger foods. Have a food allergy action plan for yourself or your allergic child. Wherever necessary you may have to carry a note with you or put in your children pocket or lunch box bag or picnic bag or purse or wallet a medical ID note indicating the allergy. Knowing more about your allergy can make living with it easier for kids and for adults.

Food Intolerance : What is it? Food Intolerance, Not an Allergy
Food intolerance does not involve a reaction of the immune system. For example, lactose intolerance is a common food intolerance. People who are lactose intolerant lack the enzyme (lactase) needed to digest sugar found in dairy (lactose). This intolerance results in gas, bloating, and abdominal pain when dairy is consumed. Some types of food intolerance, including lactose intolerance, can be treated. Over-the-counter lactase tablets can help people who are lactose intolerant to digest dairy, and many lactose-free dairy products are available. If you have trouble digesting a food — like milk or gluten — that isn’t the same as a food allergy. An allergy is caused by an immune system reaction. Food intolerance, such as lactose intolerance, can cause bloating, cramps, and diarrhea. But it doesn’t cause an immune system reaction. Lactose intolerance happens when your body can’t break down lactose, the sugar in milk and dairy products.
| Foods marked with an asterisk * are common allergens and should be introduced with care after consulting with your pediatrician | ||||
4 to 6 months |
6 to 9 months |
10 to 12 months |
12 months+ |
|
Fruits |
|
same as 4 to 6 months PLUS :
THEN
|
same as 6 to 9 months PLUS :
|
same as 10 to 12 months PLUS :
|
Cereals and Grains |
|
same as 4 to 6 months PLUS :
|
||
Veggies |
|
same as 4 to 6 months PLUS :
THEN
|
same as 6 to 9 months PLUS :
|
same as 10 to 12 months PLUS :
|
FODMAP
The term FODMAP is an acronym, deriving from “Fermentable, Oligo-, Di-, Mono-saccharides And Polyols.” These carbohydrates are commonly found in the modern western diet. The restriction of these FODMAPs from the diet has been found to have a beneficial effect for sufferers of irritable bowel syndrome and other functional gastrointestinal disorders. Image below shows the FODMAP friendly and unfriendly foods that can be refer in case children have severe bowel movement or irritable bowel syndrome.


